Welcome to Viasonix, a renowned medical device manufacturer specializing in high-end vascular physiologic systems, transcranial doppler equipment, and home care devices.
Our commitment extends globally, where we strive to support vascular markets with a broad array of advanced medical products.
We pride ourselves in not just meeting, but continually raising the bar in industry standards.
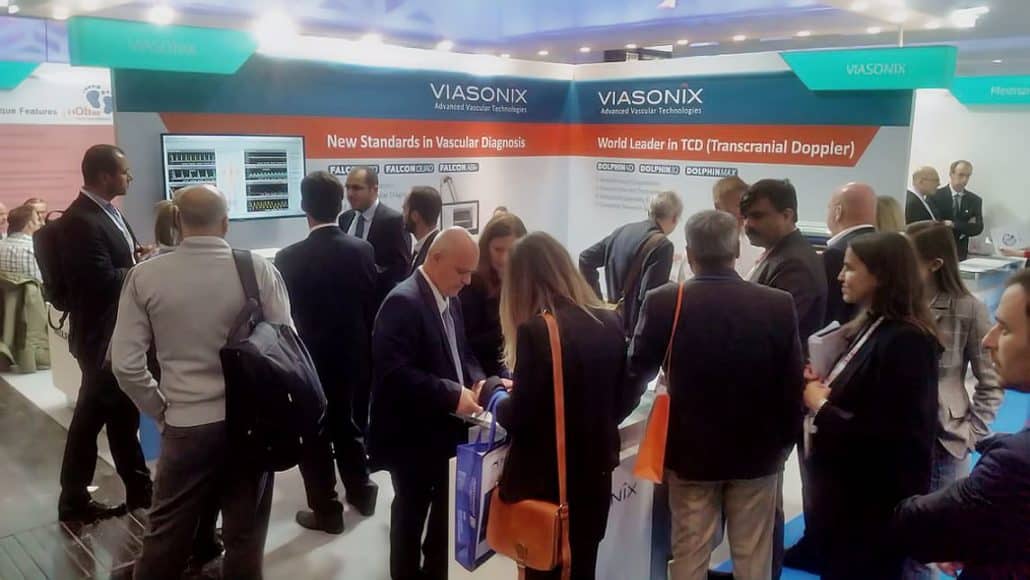

Our state-of-the-art products meet common day-to-day routine clinical practice and keep setting new industry standards.
Our professional team has decades of experience in the vascular and neuro-vascular medical fields. We particularly specialize in Doppler and Pneumatic technologies. We have successfully commercialized over the years numerous leading products such as the Sonara and Sonara-Tek TCD systems.
“At Viasonix, we take pride in providing the most advanced and comprehensive clinical solutions in the Vascular and Neuro clinical settings.
For many years our products are considered the best in their class. I invite you personally to appreciate that and join our numerous customers and business partners around the world.
Please join me on a short tour of Viasonix.”
Viasonix is ISO13485 certified, complies with the FDA QSR, and continuously maintains the highest level of a quality system. Our numerous regulatory clearances include:
At Viasonix, we never compromise on quality, and therefore, we insist on performing 100% of the activity in-house, from initial product concept through all R&D stages, production, final testing, packaging, and shipment.

Introducing to the DVT prevention market a revolutionary physiological foot compression concept based on multiple inflatable chambers.

Launching a simplified DVT prophylaxis system for supporting the fast operation by the medical staff.

Announcing the release of the unique and world’s first pneumatic dorsiflexion device for support of lower extremity blood flow in disabled populations confined to wheelchairs.

Introducing the world’s first homecare pneumatic foot compression device that is based on physiological concepts for DVT prevention and support of venous blood flow in the legs.
Stunning the Neurological clinical market with the world’s first non-invasive volume blood-flow measurement device, which is based on the self-developed and patented ADBF technology.

Expanding the clinical application of the unique ADBF technology, and designing the sterile probe for use in the operating room with a dedicated system during various surgical procedures, particularly CABG.
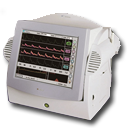
Commercializing the revolutionary dual-beam Quantix/ND, the world’s only non-invasive carotid volume blood-flow measurement system, allowing to diagnose cerebral hyperemia and hypo-perfusion quickly.
Introducing the world’s first intraoperative device for immediate volume blood-flow measurements without the need for vessel isolation. Based on state-of-the-art ultrasound Doppler and the ADBF technology.
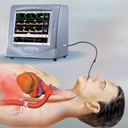
Bringing to the market the world’s first transesophageal cardiac function monitoring based on measuring volume blood flow in the Descending Aorta for the critical care setting.

Designing one of the first transcranial doppler machines in the market based on digital doppler technology. Sonara quickly becoming the world’s leader in TCD sonography.

Introducing the world’s first bilateral TCD module. Presenting the then-revolutionary concept of a TCD module that connects to an external computer for operation.
Developing the most advanced physiological 10-channel vascular diagnostic device in the market. Introducing numerous add-on features and options for the benefit of the vascular medical staff.

Launching the 4-chamber Falcon/Quad physiologic machine. Designed as the vascular workhorse for complete vascular assessment.

Releasing the fast screening Falcon/ABI+ system that allows to quickly and simultaneously complete an ABI measurement on all 4 extremities with the aid of Photo-Plethysmography technology.

Pioneering vast and extensive integrated network connectivity to Viasonix medical devices. Allowing practically simple plug-and-play connectivity with any hospital PACS system. Introducing a variety of networking options, including DICOM, HL7, GDT, Structured Reporting, Worklists, and more.
Launching the world’s most advanced standalone transcranial doppler machine. Introducing breakthrough TCD technology which allows comprehensive analysis and assessment for the benefit of clinical decision making.

Expanding the revolutionary abilities of the Dolphin technology into the TCD module market. Dolphin/IQ enjoys all of the advanced advantages of the Dolphin/4D TCD machine.
Introducing the world’s first TCD standalone system, which is completely operated by an integrated battery. This breakthrough ability is designed particularly to support bedside TCD measurements, especially in clinical settings such as the ICU.
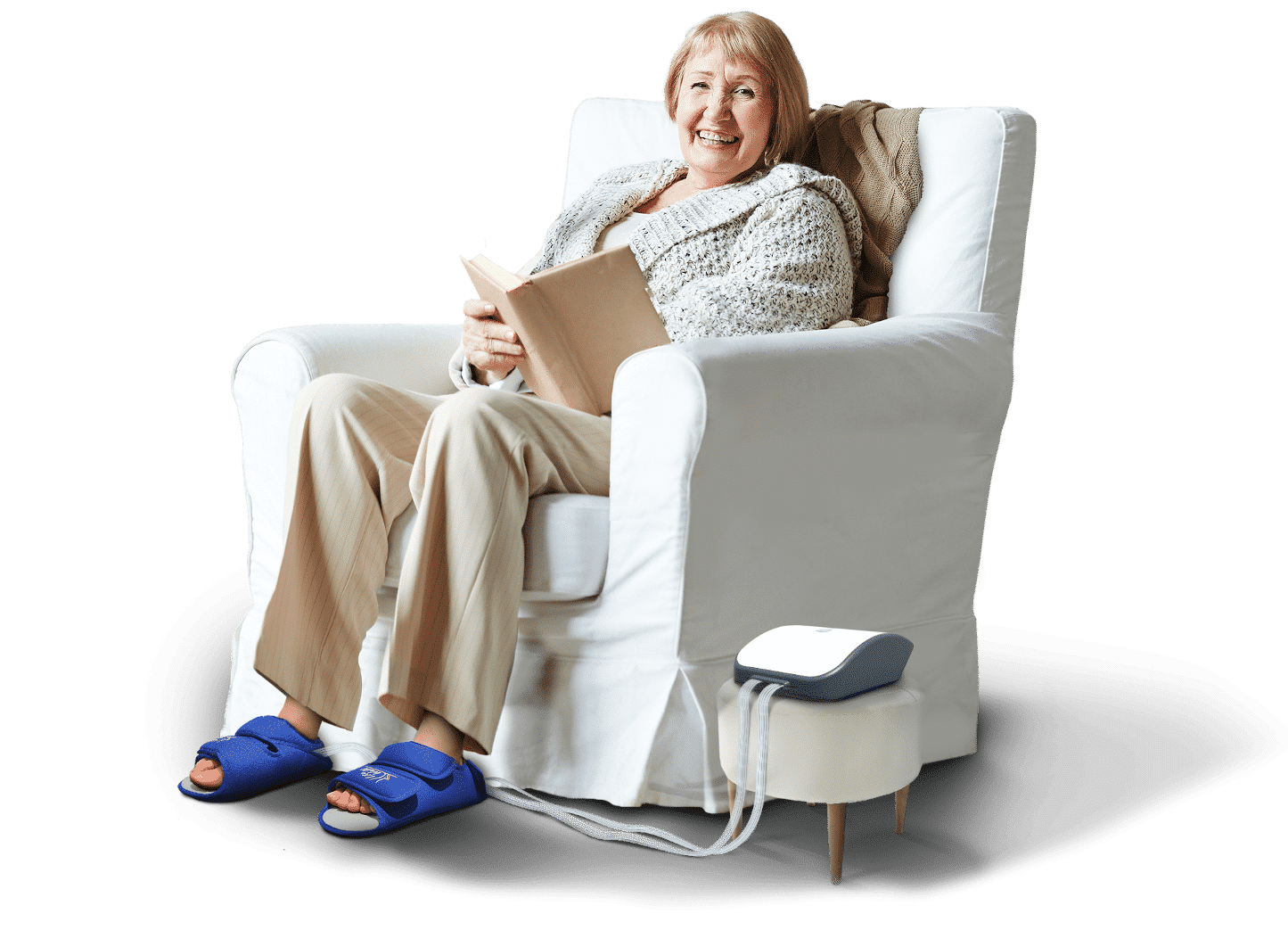

Introducing the world’s only homecare pneumatic foot compression device that mimics walking. This innovative product is designed for the elderly population and other populations with limited walking abilities to support venous blood flow through physiological mechanisms.
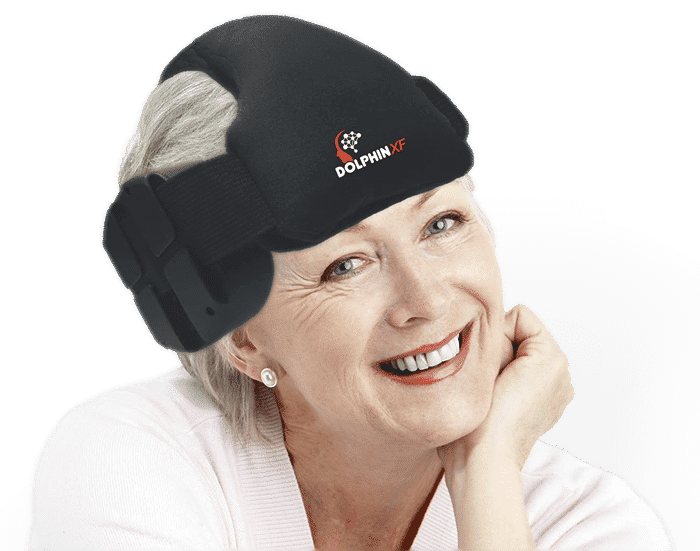

Launching the world’s most advanced and effective TCD robotic probe. Being very simple to assemble and fast and effective to operate, the Dolphin/XF TCD robot becomes a market game-changer in the TCD arena.
Expanding the wide range of PPG sensor offerings with a new design of detachable PPG clip sensors. The additional PPG line increases the company's variety of PPG options, including toe clips, finger clips, and disk sensors.
Our QA/RA Department never compromises on the highest possible quality standards for our organization and our products.
Year after year, we successfully meet all international QA and RA requirements. In addition to FDA and CE approvals for all of our products, we also support domestic regulatory certifications in numerous countries around the world.


Our Clinical Research Department is extremely active and is continuously involved with new developments and innovations year after year.
We consult with key opinion leaders in their respective fields to ensure that our products meet the highest level of expectation of the medical community.
We take particular pride in our Hardware and Electronic Board Design Department. Our engineers develop our electronic boards to meet the highest international safety standards and performance.
Our products are designed for smooth and effective real-time applications.

Our renowned software department has years of overwhelming reputation in meeting market needs and developing products which are as simple to operate as possible.
Our friendly user interface allows almost complete flexibility to meet practically every customer’s specific clinical needs.
Our Production Department is responsible for assembling and testing each and every system before it leaves our factory. This process ensures the utmost product quality without relying on third parties.
Each product is continuously monitored from the first step and until it is shipped to our customers, and the process is supported by dedicated procedures and work instructions.


Our busy Mechanical Engineering Department pays particular attention to human factor considerations when setting our product design path.
Our mechanical engineers continuously strive to develop products that are simple to use and effective. Our designs always take into consideration the medical staff and operators as well as the patients and end-users.
Our Marketing Department is busy supporting our numerous business partners around the globe, covering North and Latin America, Europe, Asia, and all the way to Australia and New Zealand.
We are also always looking for new quality distributors to join our rapidly growing international network.


Last, but definitely not least, our Service Department is always available for immediate support to ensure maximal customer satisfaction.
Our business partners know that they can rely on us 24/7 and can expect a prompt and effective response.
Contact us via email: [email protected]
Or using the form below.
Our team will respond back quickly!
Beyar, R.; Caminker, R.; Manor, D.; Sideman, S., Coronary flow patterns in normal and ischemic hearts: Transmyocardial and artery to vein distribution. Annals of Biomed.Eng., 1993. 21: p. 435-458.
Manor, D., S. Sideman, and R. Beyar, Pressure-flow characteristics of the coronary collaterals: a model study. Am. J. Physiol., 1994. 266 (Heart Circ. Physiol. 35): p. H310-H318.
Sideman, S.; Manor, D.; Zinemanas, D.; Beyar, R., Some new models relating coronary flow and myocardial contraction. J. Isr. Inst. Chem. Eng., 1993. 22: p. 62-66.
Manor, D.; Beyar, R.; Shofti, R.; Sideman, S., In vivo study of the mechanical properties of epicardial coronary arteries. J. Biomech. Eng., 1994. 116: p. 131-132.
Manor, D.; Sideman, S.; Dinnar, U.; Beyar, R., Analysis of flow in coronary epicardial arterial tree and intramyocardial circulation. Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput., 1994. 32: p. S133-S143.
Manor, D.; Sideman, S.; Dinnar, U.; Beyar, R., Analysis of coronary circulation under ischaemic conditions. Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput., 1994. 32: p. S123-S132.
Manor, D.; Shofti, R.; Sideman, S.; Beyar, R., Quantitative sorting of normal and abnormal coronary flow wave form shapes. IEEE Trans. on Biomed. Eng., 1994. 41: p. 846-853.
Manor, D.; Williams, S.; Ator, R.; Bryant, K.; Scheel, K.W., Reduced collateral perfusion is a direct consequence of elevated right atrial pressure. Am. J. Physiol., 1994. 267 (Heart Circ. Physiol. 36): p. H1151-H1156.
Amitzur, G.; Manor, D.; Pressman, A.; Adam, D.; Hammerman, H.; Shofti, R.; Beyar, R.; Sideman, S., Modulation of the arterial coronary blood flow by asynchronous activation with ventricular pacing. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol., 1995. 18(4 Pt 1): p. 697-710.
Beyar, R., Manor, D; and S. Sideman, Myocardial mechanics and coronary flow dynamics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 1993. 346: p. 125-136.
Manor, D. and K.W. Scheel, Left ventricular pressure is an important determinant of coronary oscillatory flow amplitude [letter; comment]. Am. J. Physiol., 1995. 268(5 Pt 2): p. H2162-H2165.
Manor, D.; Williams, S.; Ator, R.; Bryant, K.; Scheel, K. W., Left ventricular mechanics in arrested dog heart: effects of ventricular interaction and vascular volumes. Am. J. Physiol., 1995. 268(5 Pt 2): p. H2125-H2132.
Manor, D.; Sideman, S.; Dinnar, U.; Beyar, R., A model of the coronary epicardial tree and intramyocardial circulation in normal and ischemic hearts, in IEEE Computers in Cardiology. 1989. p. 247-250.
Beyar, R.; Manor, D.; Hallman, M.; Azhari, H.; Dinnar, U.; Lessick, J.; Sideman, S., Coronary circulatory model linked to three dimensional cardiac mechanics, in Imaging, Measurement and Analysis of the Heart, S.a.B. (Sideman, R., editors), Editor. 1990, Hemisphere Publishing Company: New York. p. 127-138.
Manor, D.; Beyar, R.; Dinnar, U.; Sideman, S., Analysis of blood flow in the normal and obstructed coronary epicardial arterial tree, in 9th Int. Heat Transfer, G.H. (editor), Editor. 1990, Hemisphere Publ.: N.Y. p. 253-256.
Manor, D.; Beyar, R.; Dinnar, U.; Sideman, S., Blood flow in the stenosed coronary circulation: Model predictions and experimental validation, in Cardiovascular System Dynamics Soc. 1990: Tiberias.
Beyar, R.; Caminker, R.; Manor, D.; Ben-Ari, R.; Sideman, S., On the mechanisms of transmural myocardial compression and perfusion, in Cardiac Electrophysiology, Circulation and Transport, S.a.B. (Sideman, R., editors), Editor. 1991, Kluer Academic Publ.: Springfield, MA. p. 245-261.
Sideman, S., Manor, D; and R. Beyar, Capacitance and resistance effects on coronary flow dynamics, in Compliance of the Cardiovascular System, V.a.K. (Starc, T., editors), Editor. 1991, Medicinski Razgledi. p. 135-139.
Manor, D., R. Beyar, and S. Sideman, On the pressure-flow relationship of the coronary collaterals: a model study, in IEEE Computers in Cardiology. 1991. p. 713-716.
Beyar, R.; Manor, D.; Zinemanas, D.; Sideman, S., Concepts and Controversies in Modeling the Coronary Circulation, in Recent Advances in Coronary Circularion Research, Y. (Maruyama, Kajiya, F., Hoffman, J.I.E. and Spaan, J.A.E., editors), Editor. 1993, Springer-Verlag: Tokyo. p. 135-149.
Beyar, R., Manor, D.; and S. Sideman, Myocardial mechanics and coronary flow dynamics, in Interacive Phenomena in the Cardiac System, S.a.B. (Sideman, R., editors), Editor. 1993, Plenum Publishing Corp.: N.Y. p. 125-136.
Manor, D.; Williams, S.; Ator, R.; Bryant, K.; Scheel, K. W., Modulation of coronary flow by left ventricular volume in the presence and absence of vasomotor tone. Am. J. Physiol., 1995. 269 (Heart Circ. Physiol. 38): p. H2010-H2016.
Scheel, K.W., Manor, D.; and K. Bryant, Influences of coronary venous pressures on left ventricular function, in Cardiac-Vascular Remodeling and Functional Interactions, Y. (Maruyama, Hori, M., Janicki, J.S., editors), Editor. 1996, Springer-Verlag: Tokyo.
Manor, D, Squential Foot Compression Devices (SFCD): Clinical Considerations. Document No. RPT-0001, June 2000.
Soustiel, J, Levy, E, Bibi, R, Lukaschuk, S, and Manor, D., Hemodynamic consequences of cerebral vasospasm on perforating arteries: A phantom model study. Stroke, 2001;32(3), p. 629-633.
Soustiel, J, Levy, E, Zaaroor M., Bibi, R, Lukaschuk, S, and Manor, D., A new angle-independent Doppler ultrasound device for the assessment of volume blood flow in the extracranial internal carotid artery. J. Ultrasound Med, 2002; 21, p. 1405-1412.