In this review, we will try to cover some of the many benefits of using traditional TCD machines over the use of an ultrasound imaging device. Such imaging equipment is also known as TCDI, color doppler ultrasound, Imaging device, Duplex, B mode imaging, TCCD, or transcranial color duplex machine.
TCD is Known as the Gold Standard for CBF Measurements
Traditional TCD machine is still the most popular device in every hospital or clinic for transcranial measurements and typically can be found in the Neurosurgery/Neurology department, in the ICU, Neuro ICU, and the operating room.
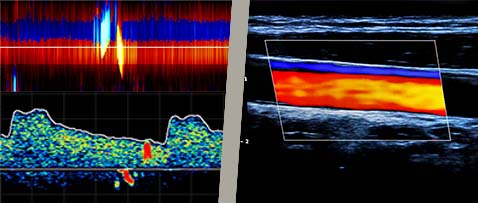
While you could use ultrasound imaging machines to perform transcranial blood flow measurements, you should know they are not dedicated to those types of applications and are mainly focused on Carotid, Cardiac, and peripheral vascular imaging.
The Benefits of TCD Over Ultrasound Imaging
According to the Society of Vascular Ultrasound (SVU), the TCD machine has better beam penetration and better vessel detection rates. This determination is in part due to the relatively smaller and lighter doppler probe. In contrast, the dimensions of an ultrasound probe are typically much larger and can result in a significant change in the measured velocity.
The smaller probe footprint of a TCD probe has a better chance of penetrating the normally small temporal windows. The temporal window, if it exists, allows measurements of blood flows within the Circle-of-Willis.
While it often seems that TCCD and TCD are competing technologies, they are actually complementary devices and are often found to work side by side in the diagnostic room.
Selected TCD Applications that You Cannot Measure with Ultrasound Devices
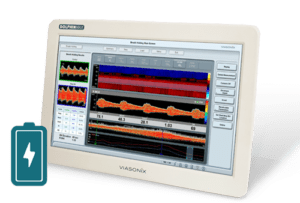
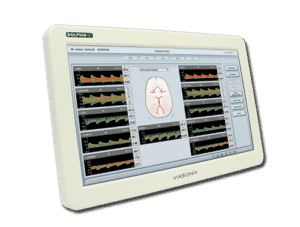
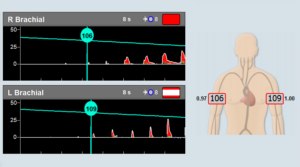
Continuous Bilateral Monitoring – a dedicated bilateral headset allows monitoring cerebral blood flow for several hours in the TCD lab, Neuro ICU, or Operating Room environments. An automated robotic headset, such as the advanced Dolphin/XF robotic probe, simplifies CBF monitoring for physicians or technicians that are less skilled for TCD measurements.
You will find that TCD bilateral monitoring is extensively used in the operating room. It is especially useful during endarterectomy, cardiac surgery, and cerebrovascular bypass.
The main clinical applications of TCD monitoring are:
- Ensure proper blood flow to the brain,
- Examine the effect of clinical and pharmacological perturbations,
- Count gaseous or solid emboli that flow towards the cerebral circulation,
- Evaluate cerebral autoregulatory capacity.
Importantly, ultrasound imaging devices don’t have any CBF monitoring capabilities and cannot be used for these standard clinical needs.
Emboli count during Patent Foramen Ovale testing – although you could use ultrasound imaging devices to diagnose PFO, they are not dedicated to this type of application. You will have to count each microbubble manually.
TCD machines, and particularly the Dolphin TCD system, have a dedicated protocol and ability to count automatically the number of microbubbles that travel to the brain. This counting is done separately for each bubble injection to assess the severity of the right to left shunt size. The latest technology in the field called “HITS Analysis” included with the Dolphin Transcranial Doppler allows analyzing each suspected emboli individually and marking HITS as artifacts or vice versa.
Ultrasound imaging devices are not designed to support this popular clinical application of PFO.
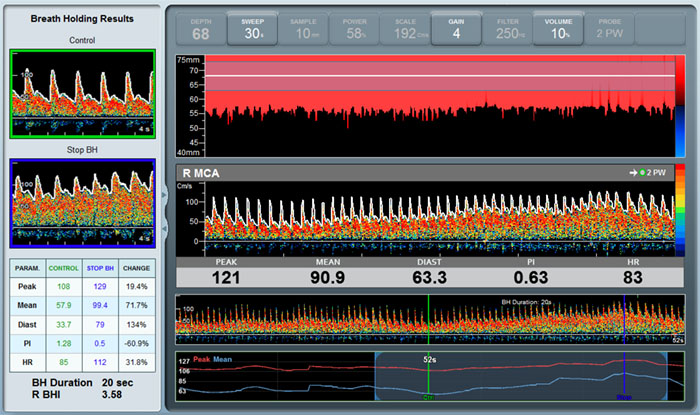
Breath Holding & Vasomotor Reactivity (VMR) – Only the traditional TCD systems allow you to get an assessment of the patient’s cerebral collateral capacity and vasomotor reactivity.
Advanced TCD devices such as the Dolphin come with dedicated monitoring headgear or a special robotic monitoring probe. These headgears help obtain a stable bilateral signal on both sides of the patient’s head. Such devices allow dedicated specialty tests protocols to guide the user through the testing procedure step by step.
Once the examination is completed, a TCD system calculates the relevant Breath Holding Index (BHI) automatically, the Vasomotor Reactivity capacity (VMR), and other parameters to save a lot of valuable examination time and improve clinical diagnosis and output.
Advantages of TCD in Size
High-end ultrasound imaging devices are typically quite bulky and include dedicated carts. These machines often occupy a lot of space, and therefore you will rarely find them on the bedside in the ICU or the operating room. Although there are portable ultrasound imaging devices, these are not intended for emboli detection and bilateral monitoring applications, which are very common in these departments.
TCD devices are typically much smaller and occupy less space. Advanced TCD machines, such as the Dolphin/MAX, are portable, lightweight, have an integrated display rechargeable battery. Such designs make it ideal for bedside CBF measurement.
Advantages of TCD in Cost
The pricing range of ultrasound imaging equipment compared to the price of a Transcranial Doppler machine is another important factor. Even the higher-end TCD machines are usually much more cost-effective than high-end ultrasound imaging devices.
So how much does a Transcranial Doppler machine cost? It depends on specific models, configurations, software packages, network connectivity, and training days. Please feel free to let us know your needs, and we will provide you with Transcranial Doppler pricing information.
Advantages of TCD in Terms of Operation
As we all know, the operation of an ultrasound machine is quite complex and requires a skilled and professional sonographer to operate such a unit. The operators need to know how to change from B-Mode to M-mode and zoom in to specific “interesting” locations until they get all the required information and all that while holding the probe on the measured vessel.
TCD examinations are much simpler, although still requiring a skilled sonographer to operate. It really all depends on the user-friendliness of the TCD device. Take the Dolphin TCD machine as an example, which has an intuitive and world-renowned user interface. Such a device will guide the sonographer through the protocol phases and make the Transcranial Doppler operation of the TCD system very simple. Also, it will include both Power M-Mode, and Phasic M-Mode displays to help the sonographer to find the desired cerebral blood vessel quickly.
Final Words
We are now entering the 40th year of the introduction of traditional TCD technology!
TCD is not only still relevant and popular, but it is also evolving with the addition of new innovations and technologies such as robotic probes, HITS Analysis, and direct connectivity to EMR.
For more information, please leave us a message.